-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 26
Kyrix‐S API Reference
Kyrix-S is an extension to the core Kyrix system, providing a simple declarative grammar for authoring large-scale zooming-based scatterplots, which we call Scalable Scatterplot Visualizations (or SSV). Kyrix-S's declarative grammar is a high-level concise grammar built on top of the lower-level Kyrix grammar, which enables authoring of a complex SSV in tens of lines of JSON.
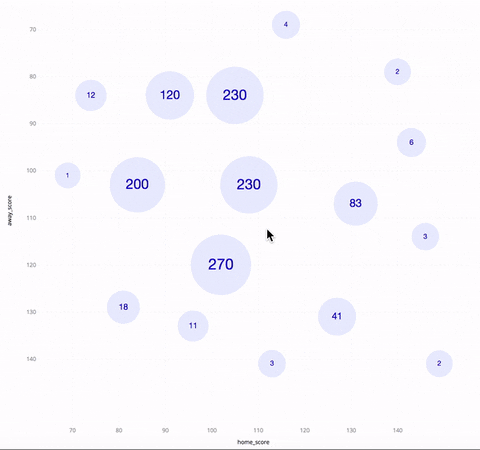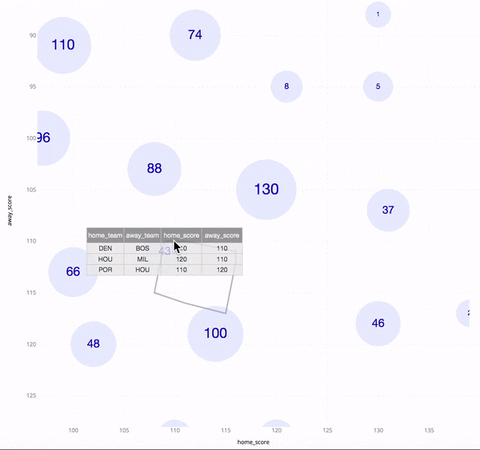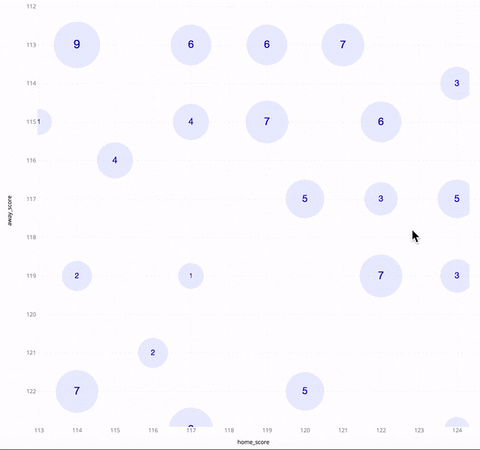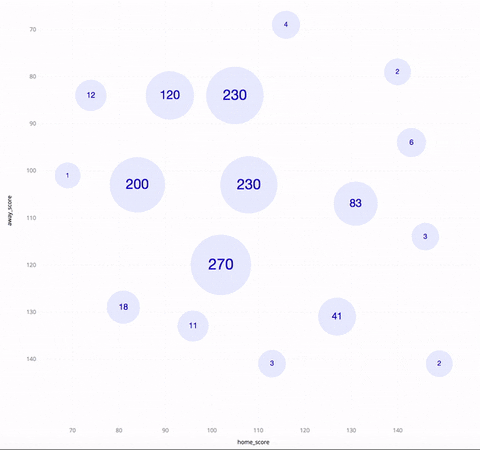
The above GIF shows an SSV of NBA basketball games in the season of 2017~2018. The horizontal/vertical axis is the score of the home/away team. Each circle represents a cluster of games, with the number inside it being the cluster size. As one zooms in, the circles get collapsed into a bunch of smaller circles. When you hover over a circle, you see three games between the highest-ranked teams in that cluster, as well as a polygon indicating the boundary of the cluster.
To author this SSV using Kyrix-S, you only need to write the following JSON specification:
{
data: {
db: "nba",
query: “SELECT * FROM games"
},
layout: {
x: {
field: "home_score",
extent: [69, 149]
},
y: {
field: "away_score",
extent: [69, 148]
},
z: {
field: "agg_rank",
order: "asc"
}
},
marks: {
cluster: {
mode: "circle"
},
hover: {
rankList: {
mode: "tabular",
fields: ["home_team", "away_team", "home_score", "away_score"],
topk: 3
},
boundary: "convexhull"
}
},
config: {
axis: true
}
};Run the following commands in the root folder to bring up this application after the docker containers are started:
> cd compiler/examples/template-api-examples
> cp ../../../docker-scripts/compile.sh compile.sh
> chmod +x compile.sh
> sudo ./compile.sh SSV_circle.js
More examples can be found here.
An an extension, Kyrix-S interoperates with Kyrix through the Project.addSSV call. By passing a JSON specification of an SSV into Project.addSSV, you can add one SSV into an encompassing Kyrix application, either as a new set of canvases, or a set of new layers of existing canvases. For more details, please refer to the Kyrix API reference. We document how to specify an SSV in JSON down below.
There are several components in this grammar, some of which have subcomponents. Here we provide a detailed description.
-
data: defines the data being visualized.-
query: a SQL query to fetch data for the SSV. Each record in the query result should correspond to one object in the scatterplot. -
db: the database in whichdata.queryshould be run. -
columnNames: an optional array specifying the field names for the query results. This is used in specifying layout-related information, aggregation or tooltips. If not specified, Kyrix-S will use the column names returned by the database.
-
-
layout: controls the placement of the marks in the multi-scale zooming space.-
x: defines the horizontal axis of the SSV.-
field: a quantitative field in the query result that maps to the horizontal axis of the SSV. This should be one ofdata.columnNames(if specified), or one of the column names returned in the query results by the database. -
extent: an optional two-number array[a, b]indicating the visible range of the field.acan be larger thanb. If not specified, min/max value ofx.fieldwill be used as the visible range.
-
-
y: defines the vertical axis of the SSV.-
field: a quantitative field in the query result that maps to the vertical axis of the SSV. This should be one ofdata.columnNames(if specified), or one of the column names returned in the query results by the database. -
extent: an optional two-number array[a, b]indicating the visible range of the field.acan be larger thanb. If not specified, min/max value ofx.fieldwill be used as the visible range.
-
-
z: defines how objects are distributed across zoom levels. -
overlap: a number between 0 and 1 indicating how much overlap between objects is desired, with 0 meaning arbitrary overlap is allowed and 1 meaning no overlap is allowed. Note that this only sets the lower bound on the amount of overlap. Kyrix-S will space the objects more if visual density becomes too high in some regions.
Note that null values in layout.x.field, layout.y.field and layout.z.field will be regarded as 0. So make sure the missing values in the data are properly imputed.
-
-
marks: defines the visual representation of one or more objects, and is consisted of two components,clusterandhover.-
cluster: cluster marks are static marks rendering one or a cluster of objects.-
mode: defines one of the five types of visual marks:circle,heatmap,radar,pieorcustom. The last modecustomrequires a custom renderer (see marks.cluster.custom), and the maximum width/height of an object (see marks.cluster.config.bboxW). -
aggregate: defines the aggregation information needed to render a cluster of objects, and is consisted of an array ofmeasuresanddimensions, which together forming a SQL aggregation query.-
measures: defines what aggregation statistics to be calculated and on what fields, and is optional. If not specified, by default Kyrix-S computescount(*)for each cluster of objects. If specified, it should be an array with each element being an object with the following fields:-
field: name of the field on which this aggregation statistic is calculated, which should be either*when specifyingcount, or a quantitative field from the query results. -
function: the aggregation statistic to be calculated, and can be one ofcount,sum,avg,min,maxandsqrsum. -
extent: an optional two-number array specifying the range of the calculated aggregation statistic. Required forradar.
In the case where you want to specify the same function for many fields, you can instead specify this component as an object, with
fieldbeing an array of field names,functionbeing the aggregation statistic, andextentbeing the range for all measures. See here for an example. For modescircle,heatmapandpie, at most one measure can be specified. -
-
dimensions: defines how objects are grouped when calculating aggregation statistics, and is optional. If not specified, no grouping is performed. If specified, it should be an array with each element being an object with the following fields:-
field: name of the field of a grouping column, which should be a categorical field from the query results. -
domain: an array of strings indicating all possible values offield.
For modes
circle,heatmapandradar, grouping is not supported. So you do not need to specifydimensionsfor those modes. -
-
-
custom: a rendering functionf(svg, data, args)for thecustommode which converts a set of data itemsdatato visual marks, and attaches them tosvg. Each data item indatais the representative object of a cluster of objects, with an additional fieldclusterAggcontaining aggregation statistics of this cluster. To access the size of the cluster, you can writed.clusterAgg["count(*)"]wheredis the data item. If there is grouping, you can writed.clusterAgg["medical_male_avg(salary)"], which is the average salary of male employees in the medical department in this cluster.argsis a dictionary containing lots of useful information about the encompassing Kyrix application, similar to the input of a Kyrix layer renderer. An example. -
config: a set of optional parameters for customizing the looks of the cluster marks.-
bboxW: the width of the bounding box of all cluster marks. You need to specify this if and only if you are using thecustommode. -
bboxH: the height of the bounding box of all cluster marks. You need to specify this if and only if you are using thecustommode. -
circleMinSize: the minimum size of the circles in thecirclemode. Default is -
circleMaxSize: the maximum size of the circles in thecirclemode. -
heatmapRadius: the radius of an object in theheatmapmode. -
heatmapOpacity: the opacity of heatmaps in theheatmapmode. -
radarRadius: the radius of a radar in theradarmode. -
radarTicks: the number of ticks on an axis of a radar in theradarmode. -
pieInnerRadius: the inner radius of a pie in thepiemode. -
pieOuterRadius: the outer radius of a pie in thepiemode. -
pieCornerRadius: the corner radius of a pie in thepiemode. -
padAngle: the amount of padding between pies in thepiemode.
-
-
-
hover: hover marks are shown when the user mouses over a cluster mark. This component is optional.-
rankList: hover marks that show representative objects from a cluster. The ranking of objects is defined inlayout.z. Cannot be specified together withmarks.hover.tooltip.-
mode: eithertabularwhich displays representative objects in a table, orcustom, which is used to customize how objects are rendered. Forcustom,bboxWandbboxHmust be specified inmarks.hover.rankList.configindicating the size of the bounding box of an object. -
topk: an integer greater than 0, indicating how many representative objects are displayed upon hovering. -
fields: an array of fields that will be displayed in thetabularmode. -
custom: the custom renderer for thecustommode. See more descriptions at marks.cluster.custom. -
orientation: the direction in which representative objects are positioned, could be eitherhorizontalorvertical. -
config: a set of optional parameters for customizing the looks of the hover marks.-
bboxW: the width of the bounding box of acustomhover mark. Required for thecustommode. -
bboxH: the height of the bounding box of acustomhover mark. Required for thecustommode. -
hoverTableCellWidth: the width of a cell in thetabularmode. Default is 100. -
hoverTableCellHeight: the height of a cell in thetabularmode. Default is 50.
-
-
-
tooltip: shows simple tooltips about a cluster, instead of a ranked list of objects. Cannot be specified together withmarks.hover.rankList.-
columns: an array of fields of the representative object to be displayed. The fields should exist indata.columnNamesif it is specified, or in the result returned bydata.query. -
aliases: an array of aliases for the fields specified incolumns. Should have the same number of elements ascolumns.
-
-
boundary: hover marks that show the boundary of clusters. Can be eitherbbox, which shows the boundary as the boundingbox, orconvexhull, which shows a polygonal enclosure of the cluster.
-
-
-
config: a set of optional global parameters for customizing the SSV.-
axis: a boolean representing whether axes are displayed. Default tofalse. -
xAxisTitle: the title of the x axis. Default tolayout.x.field. -
yAxisTitle: the title of the y axis. Default tolayout.y.field. -
numLevels: number of zoom levels in the SSV. Default to 10. -
topLevelWidth: width of the top level. Default to 1000. -
topLevelHeight: height of the top level. Default to 1000. -
zoomFactor: zoom factor between adjacent levels. Default to 2. -
legendTitle: title of the legend panel. Default to"legend". Currently only applicable in pie charts. -
legendDomain: domain of the legends. Should be specified as an array of strings. If not specified, Kyrix-S will use all distinct combinations of domains as the domain for the legends. Currently only applicable in pie charts.
-
In the current release, Kyrix-S only works on a single node with sufficient main memory that can hold all data. To allocate memory to the kyrix container , run the following:
> sudo ./run-kyrix.sh --mavenopts -Xmx700m # allocate 700MB memory to the kyrix container
if not specified, the default memory allocated is 512MB. Generally, if the size of raw data is X, you'll need to allocate 10X memory to the kyrix container.
We do have a multi-node Kyrix-S that can scale to billions of objects. We are working on testing it more thoroughly and include it in a future release. Stay tuned!