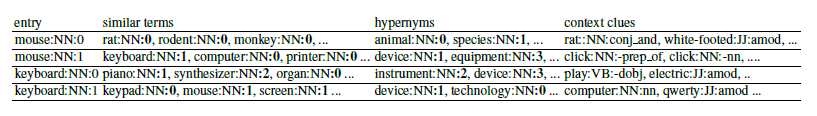
Disambiguated Distributional Semantic-based Sense Inventories are hybrid knowledge bases that combines the contextual information of distributional models with the conciseness and precision of manually constructed lexical networks. In contrast to dense vector representations, our resource is human readable and interpretable, and can be easily embedded within the Semantic Web ecosystem. Manual evaluation based on human judgments indicates the high quality of the resource, as well as the benefits of enriching top-down lexical knowledge resources with bottom-up distributional information from text.
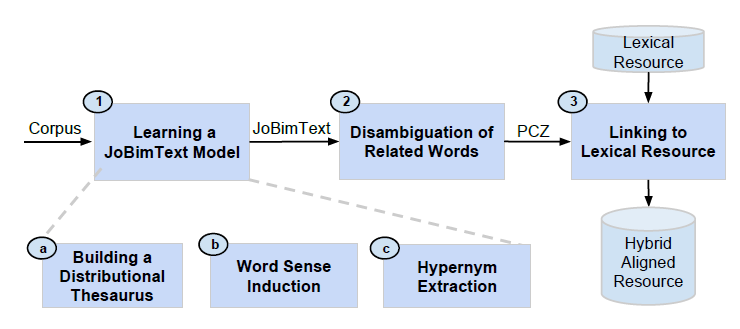
Our approach consists of three main phases:
- Learning a JoBimText model: initially, we automatically create a sense inventory from a large text collection using the pipeline of the JoBimText project.
- Disambiguation of related words: we fully disambiguate all lexical information associated with a proto-concept, i.e., similar terms and hypernyms, based on the partial disambiguation from the previous step. The result is a proto-conceptualization (PCZ). In contrast to a term-based distributional thesaurus (DT), a PCZ consists of sense-disambiguated entries, i.e., all terms have a sense identifier.
- Linking to a lexical resource: we align the PCZ with an existing lexical resource (LR). That is, we create a mapping between the two sense inventories and then combine them into a new extended sense inventory, our hybrid aligned resource. Finally, to obtain a truly unified resource, we link the “orphan” PCZ senses for which no corresponding sense could be found by inferring their type in the LR.
We provide the source code for the linking with BabelNet and WordNet.
-
Prerequirements
In order to correctly execute the linking procedure please follow this three steps:
-
1) Thesauri serializtions
serializeThesaurus.sh FOLDER GZIPPEDTHESAURUS
2) BabeblNet following the instructions from http://babelnet.org/ download the Java API and the lastest index distribution. Copy both the API jar and the "config" folder into the project folder "dist/lib/"; 3) WordNet download the lastest WordNet distribution from https://wordnet.princeton.edu/ and install the resource in some specific folder WORDNETFOLDER (e.g. "/opt/WordNet-3.1/") 4) run `install-deps.sh` to install the BabelNet JARs into your local Maven repository.
-
Link to BabelNet:
execute linker2BN.sh FOLDER FILE ITERATIONS
Link to WordNet:
execute linker2WN.sh FOLDER FILE ITERATIONS WORDNETFOLDER
This software uses BabelNet API of version 2.5.1 that is not distributed via Maven. However, it is necessary to install three dependencies: babelnet-api, jlt, and jwi.
$ cd BabelNet-API-2.5.1
$ mvn install:install-file -Dfile=lib/jlt-1.0.0.jar -DgroupId=it.uniroma1.lcl -DartifactId=jlt -Dversion=1.0.0 -Dpackaging=jar
$ mvn install:install-file -Dfile=lib/jwi-2.1.4.jar -DgroupId=edu.mit -DartifactId=jwi -Dversion=2.1.4 -Dpackaging=jar
$ mvn install:install-file -Dfile=babelnet-api-2.5.1.jar -DgroupId=it.uniroma1.lcl.babelnet -DartifactId=babelnet-api -Dversion=2.5.1 -Dpackaging=jarThese JARs can be found in an unofficial Maven repo at http://backingdata.org/mavenRepo/it/uniroma1/lcl/ (this resource is neither created nor maintained by us).