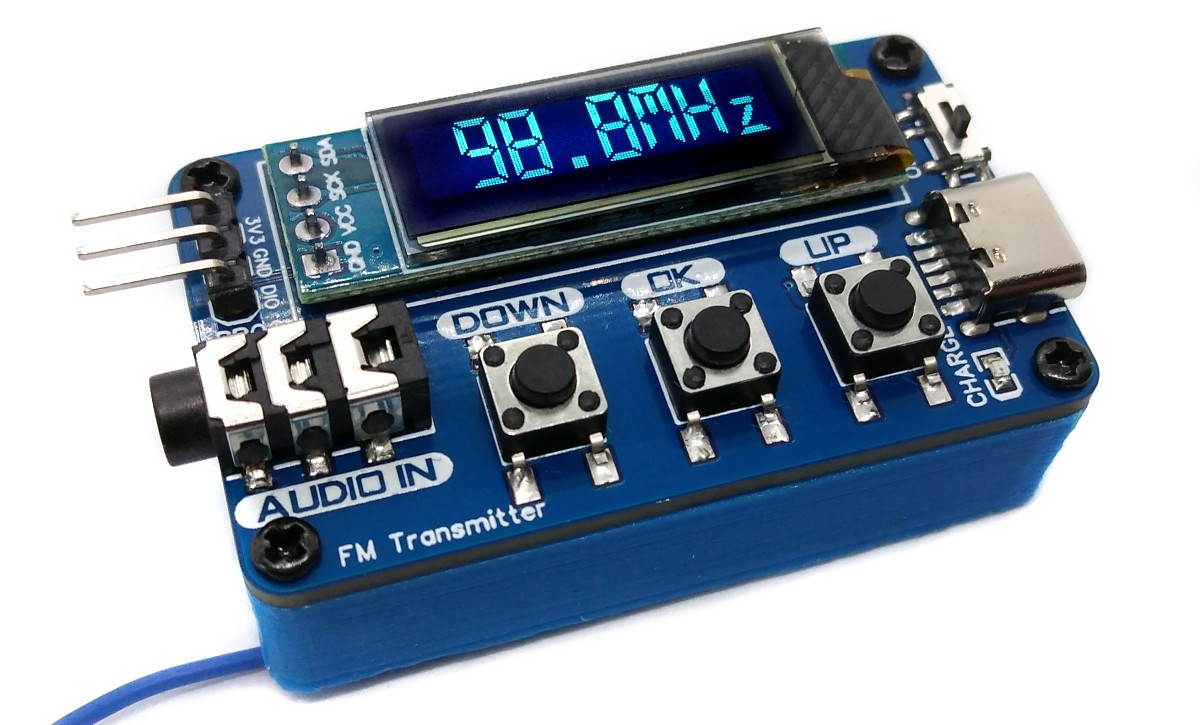
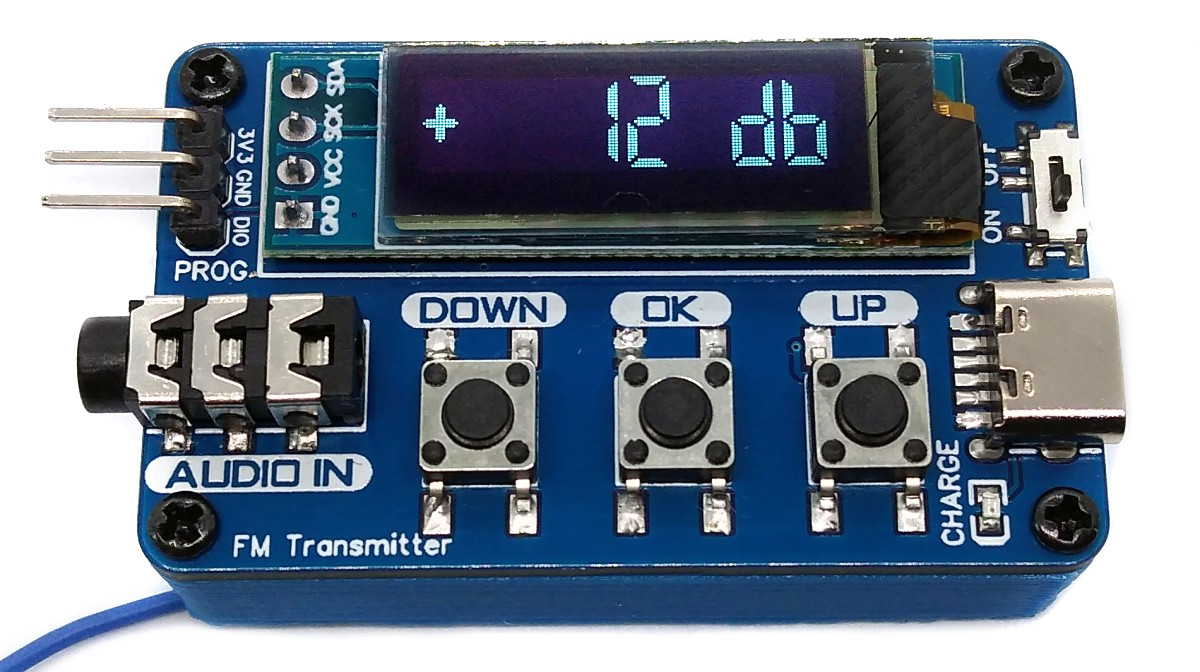
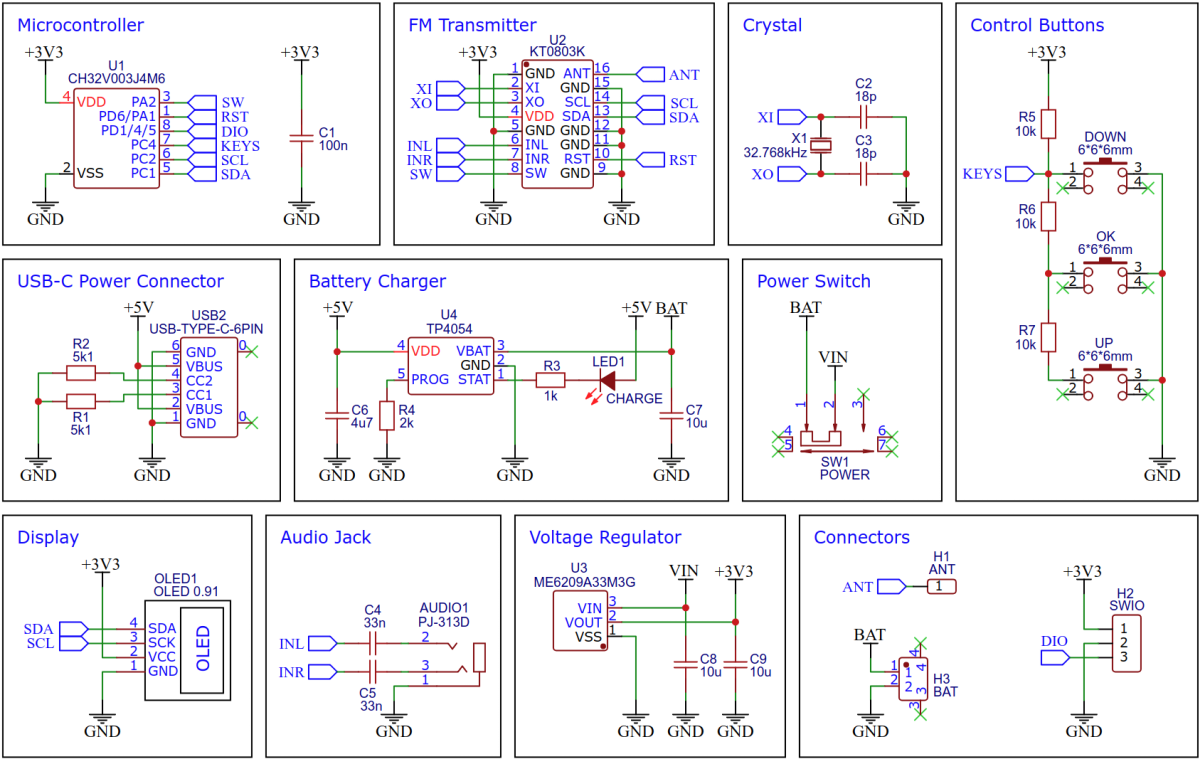
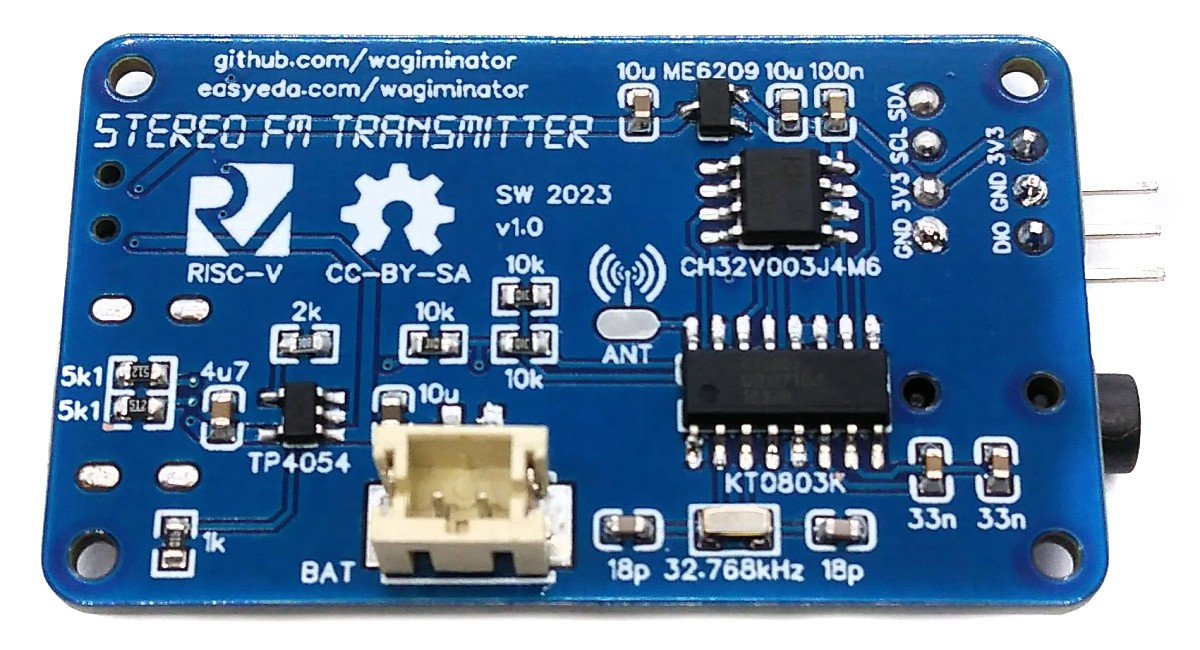
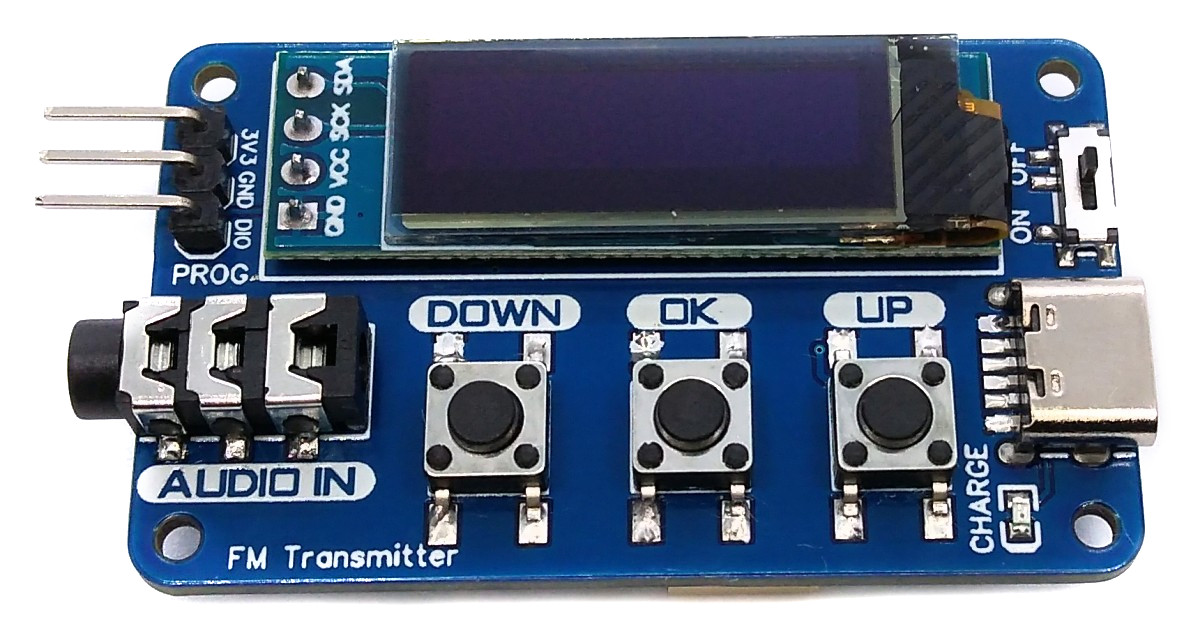
With the portable Li-Ion battery powered Stereo FM Transmitter you can transmit audio of any kind. Simply plug your audio source into the 3.5mm audio jack, set the desired frequency, and then tune any standard FM radio receiver to receive the signal. This device is equipped with cost-effective components, including a CH32V003J4M6 32-bit RISC-V microcontroller, a KT0803K/L transmitter IC, a 128x32 pixel OLED display (SSD1306), and a Li-Ion battery charger (TP4054).
The CH32V003 series is a collection of industrial-grade general-purpose microcontrollers that utilize the QingKe RISC-V2A core design supporting the RV32EC instruction set. These microcontrollers are equipped with various features such as a 48MHz system main frequency, 16KB flash, 2KB SRAM, 2.7V - 5.5V supply voltage support, a single-wire serial debug interface, low power consumption, and an ultra-small package. Additionally, the CH32V003 series includes a built-in set of components including a DMA controller, a 10-bit ADC, op-amp comparators, multiple timers, and standard communication interfaces such as USART, I2C, and SPI.
The KT0803K/L is a low cost Monolithic Digital Stereo FM Transmitter, designed to process high-fidelity stereo audio signal and transmit modulated FM signal over a short range. The KT0803K/L features dual 20-bit ΔΣ audio ADCs, a high-fidelity digital stereo audio processor and a fully integrated radio frequency (RF) transmitter. An on-chip low-drop-out regulator (LDO) allows the chip to be integrated in a wide range of low-voltage battery-operated systems with power supply ranging from 1.6V to 3.6V. The KT0803K/L can be controlled via its I²C interface.
The TP4054 is a complete constant-current/constant-voltage linear charger for single cell lithium-ion batteries. Its small package and low external component count make the TP4054 ideally suited for portable applications.
The ME6209 series are a group of positive voltage output, three–pin regulator, that provide a high current (max 250mA) even when the input/output voltage differential is small (80mV dropout voltage). Low power consumption (3µA quiescent current) and high accuracy (+/-2%) is achieved through CMOS technology. They allow input voltages as high as 18V.
A low-cost SSD1306 4-pin I2C 128x32 pixels 0.91-inch OLED module is used as the display device. Make sure to acquire one with the correct pinout!
- Take the Gerber files (the zip file inside the hardware folder) and upload them to a PCB (printed circuit board) manufacturer of your choice (e.g., JLCPCB). They will use these files to create the circuit board for your device and send it to you.
- Once you have the PCB, you can start soldering the components onto it. Use the BOM (bill of materials) and schematic as a guide to make sure everything is connected correctly. You can find the corresponding files in the hardware folder. Remove the plastic part from the pin header of the OLED, trim the pins, and solder the OLED module flush onto the PCB. Solder the wire antenna to the corresponding pad on the board. A 75cm (30" = λ / 4) long 28AWG flexible silicone insulated wire works very well.
- Upload the firmware by following the instructions in the next section (see below).
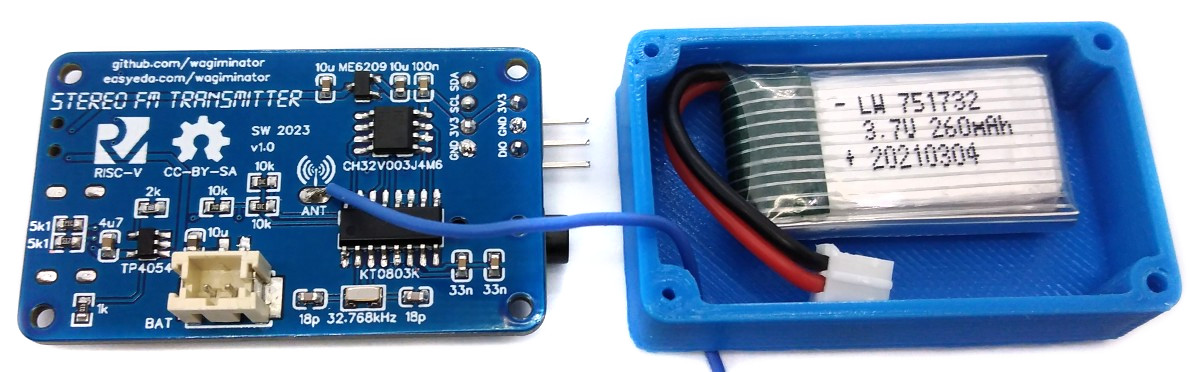
- To create the case for your device, use the stl files in the 3dprint folder with your 3D printer. Glue the battery into the case with double-sided tape. Thread the wire antenna through the small hole in the housing.
- Connect the battery to the JST connector on the board. Pay attention to the correct polarity, unfortunately there is no standard here! Place the board on the case and screw it with four M2x5mm self-tapping screws.
To program the CH32V003 microcontroller, you will need a special programming device which utilizes the proprietary single-wire serial debug interface (SDI). The WCH-LinkE (pay attention to the "E" in the name) is a suitable device for this purpose and can be purchased commercially for around $4. This debugging tool is not only compatible with the CH32V003 but also with other WCH RISC-V and ARM-based microcontrollers.
To use the WCH-LinkE on Linux, you need to grant access permissions beforehand by executing the following commands:
echo 'SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTR{idProduct}=="8010", MODE="666"' | sudo tee /etc/udev/rules.d/99-WCH-LinkE.rules
echo 'SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTR{idProduct}=="8012", MODE="666"' | sudo tee -a /etc/udev/rules.d/99-WCH-LinkE.rules
sudo udevadm control --reload-rules
On Windows, if you need to you can install the WinUSB driver over the WCH interface 1 using the Zadig tool.
To upload the firmware, you need to ensure that the FM Transmitter is switched off or the battery is removed. Then, you should make the following connections to the WCH-LinkE:
WCH-LinkE FM Transmitter
+-------+ +-------+
| SWDIO| <--> |DIO |
| GND| ---> |GND |
| 3V3| ---> |3V3 |
+-------+ +-------+
If the blue LED on the WCH-LinkE remains illuminated once it is connected to the USB port, it means that the device is currently in ARM mode and must be switched to RISC-V mode initially. There are a few ways to accomplish this:
- You can utilize the Python command-line tool rvprog (with -v option).
- Alternatively, you can select "WCH-LinkRV" in the software provided by WCH, such as MounRiver Studio or WCH-LinkUtility.
- Another option is to hold down the ModeS button on the device while plugging it into the USB port.
More information can be found in the WCH-Link User Manual.
Install the toolchain (GCC compiler, Python3, and rvprog):
sudo apt install build-essential libnewlib-dev gcc-riscv64-unknown-elf
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip
pip install rvprog
Switch off the FM Transmitter or remove the battery. Connect the FM Transmitter via the 3-pin PROG header to the WCH-LinkE programming device. Open a terminal and navigate to the folder with the makefile. Run the following command to compile and upload:
make flash
Follow the instructions on CNLohr's ch32v003fun page to set up the toolchain on your respective operating system (for Windows, use WSL). Also, install Python3 and rvprog. Compile and upload with "make flash". Note that I only have Debian-based Linux and have not tested it on other operating systems.
- Install PlatformIO and platform-ch32v. Follow these instructions to do so. Linux/Mac users may also need to install pyenv.
- Click on "Open Project" and select the firmware folder with the platformio.ini file.
- Switch off the FM Transmitter or remove the battery. Connect the FM Transmitter via the 3-pin PROG header to the WCH-LinkE programming device. Then click "Upload".
WCH offers the free but closed-source software WCH-LinkUtility to upload the precompiled hex-file with Windows. Select the "WCH-LinkRV" mode in the software, open the fm_transmitter.hex file in the bin folder and upload it to the microcontroller.
Alternatively, there is an open-source tool called minichlink developed by Charles Lohr (CNLohr). It can be used with Windows, Linux and Mac.
If you have installed Python3 on your system, you can also use the platform-independent open-source command-line tool rvprog for uploading:
rvprog -f bin/fm_transmitter.bin
- Make sure that the wire antenna is laid as straight as possible horizontally or vertically.
- Turn on the transmitter using the power switch.
- Use the OK key to switch between transmitter frequency and audio gain display/control mode.
- Use the UP or DOWN key to increase/decrease frequency/gain.
- If the battery is weak, recharge it via the USB-C port.
If you don't have an FM radio receiver and/or you want to build one yourself, take a look here.
- EasyEDA Design Files
- CNLohr: ch32003fun
- WCH: CH32V003 datasheets
- WCH: WCH-Link user manual
- WCH: Official Store on AliExpress
- KTMicro: KT0803K datasheet
- KTMicro: KT0803L datasheet
- Microne: ME6209 datasheet
- TP4054 datasheet
- SSD1306 datasheet
- 128x32 OLED on Aliexpress
- CH32V003 FM Radio Receiver
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)