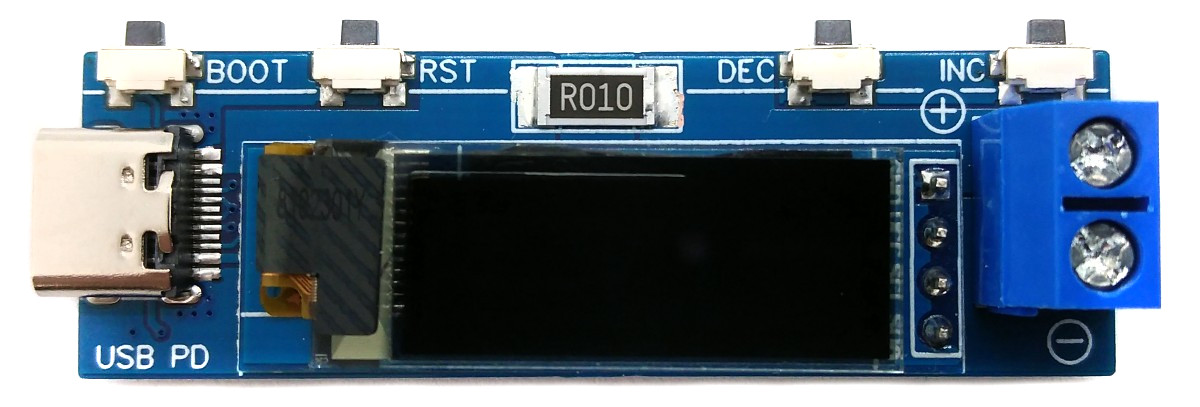
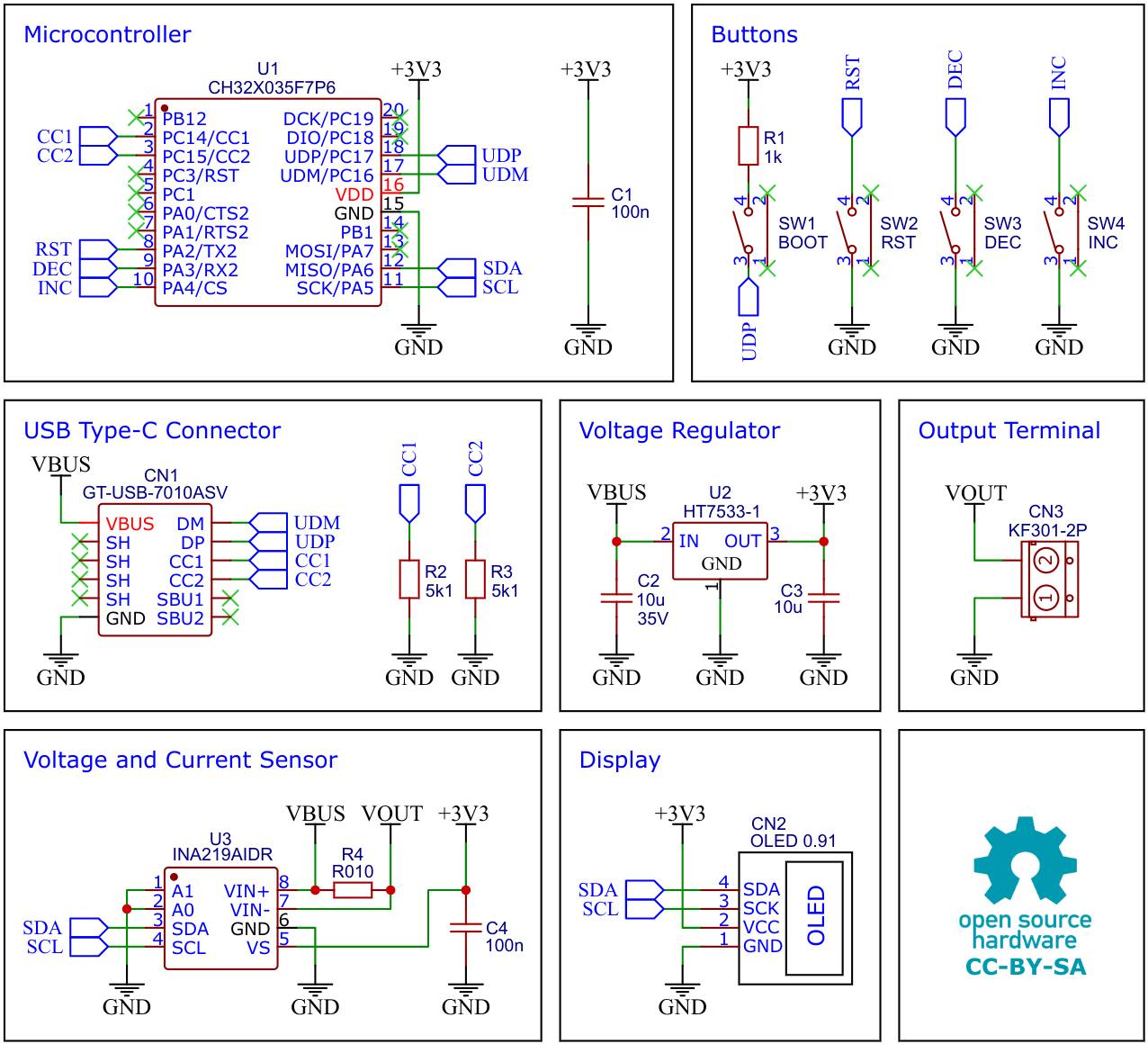
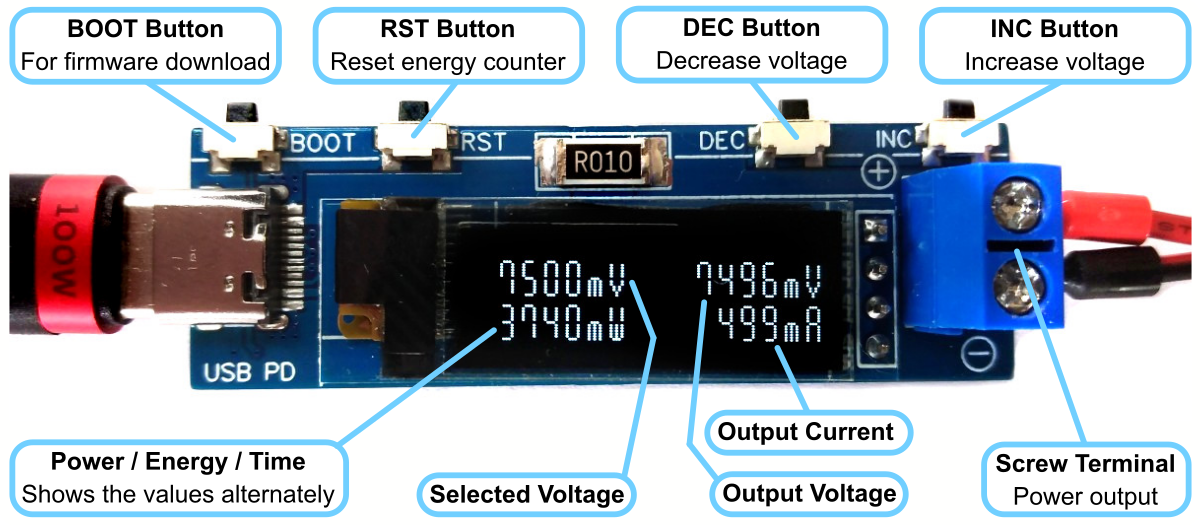
The USB PD Adapter is a compact variable power supply capable of utilizing nearly any USB Type-C PD power supply with PPS-feature as an input to power your projects with various selectable voltages and high currents. Key parameters such as voltage, current, power, and energy are conveniently displayed on the OLED screen. This adapter is built around the cost-effective (30 cents at the time of writing) and user-friendly CH32X035 32-bit RISC-V microcontroller, which features hardware USB PD support, along with the INA219 voltage and current sensor IC.
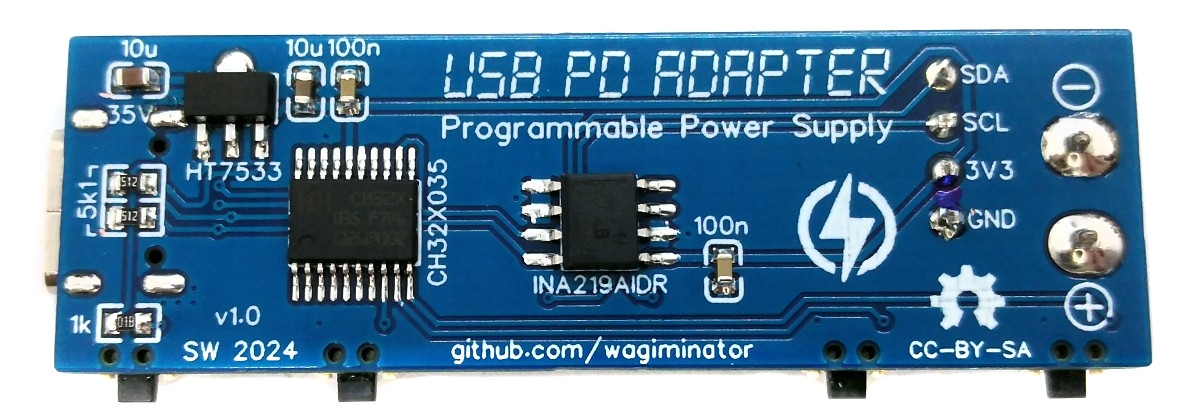
CH32X035F7P6 is a low-cost microcontroller that utilizes the QingKe 32-bit RISC-V4C core, supporting the RV32IMAC instruction set along with self-extending instructions. This microcontroller comes with a built-in USB PHY, supporting USB2.0 full-speed device functions and a USB PD PHY with source and sink capabilities. It features a programmable protocol I/O controller (PIOC), an operational amplifier (OPA) with programmable gain (PGA), an analog comparator (CMP), a 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC), an 11-channel touch-key controller, 3 groups of USART, I2C, SPI, multiple timers, and various other peripheral resources. The device can operate at clock frequencies of up to 48MHz and is compatible with a supply voltage range of 2.0V to 5.5V. The CH32X035F7P6 includes 48KB of flash, 20KB of SRAM, and an embedded USB bootloader.
The CH32X035 microcontroller manages several tasks, including power negotiation with the USB PD power supply, INA219 management, user interface control, and computation and presentation of measured values. The user interface is comprised of three buttons and an SSD1306 I²C OLED display with a resolution of 128x32 pixels.
The INA219 is a current shunt and power monitor with an I²C-compatible interface. The device monitors both the shunt voltage drop and bus supply voltage, with programmable conversion times and filtering. A programmable calibration value, combined with an internal multiplier, enables direct readouts of current in amperes.
The selected shunt resistance of 10mΩ enables both a very small influence on the circuit and a measurement with a resolution of 1mA. For accurate measurement, a shunt resistor with a low tolerance (1% or better) should be selected. The INA219 is used here to measure the output voltage and output current. It communicates with the MCU via I²C.
The HT75xx-1 series comprises three-terminal high current low voltage regulators crafted using CMOS technology. They are capable of delivering an output current of 100mA and can handle input voltages as high as 30V. The utilization of CMOS technology guarantees minimal voltage drop and low quiescent current.
The HT7533-1 provides a stable 3.3V supply to all components of the circuit. Ensure that you select a version with a maximum input voltage rating of 30V.
A low-cost SSD1306 4-pin I2C 128x32 pixels 0.91-inch OLED module is used as the display device. Make sure to acquire one with the correct pinout!
- Take the Gerber files (the zip file inside the hardware folder) and upload them to a PCB (printed circuit board) manufacturer of your choice (e.g., JLCPCB). They will use these files to create the circuit board for your device and send it to you.
- Once you have the PCB, you can start soldering the components onto it. Use the BOM (bill of materials) and schematic as a guide to make sure everything is connected correctly. You can find the corresponding files in the hardware folder. Remove the plastic part from the pin header of the OLED, trim the pins, and solder the OLED module flush onto the PCB.
- Upload the firmware by following the instructions in the next section (see below).
On Linux you do not need to install a driver. However, by default Linux will not expose enough permission to upload your code with the USB bootloader. In order to fix this, open a terminal and run the following commands:
echo 'SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="4348", ATTR{idProduct}=="55e0", MODE="666"' | sudo tee /etc/udev/rules.d/99-ch55x.rules
echo 'SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTR{idProduct}=="55e0", MODE="666"' | sudo tee -a /etc/udev/rules.d/99-ch55x.rules
sudo udevadm
For Windows you can use the Zadig tool to install the correct driver. Here, click "Options" -> "List All Devices" and select the USB module. Then install the libusb-win32 driver. To do this, the board must be connected and the microcontroller must be in bootloader mode.
The bootloader must be started manually for new uploads. To do this, the board must first be disconnected from the USB port. Now press the BOOT button and keep it pressed while reconnecting the board to the USB port of your PC. The chip now starts in bootloader mode, the BOOT button can be released and new firmware can be uploaded via USB within the next couple of seconds.
Install the toolchain (GCC compiler, Python3, and chprog):
sudo apt install build-essential libnewlib-dev gcc-riscv64-unknown-elf
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip
pip install chprog
Open a terminal and navigate to the folder with the makefile. Press the BOOT button and keep it pressed while connecting the board to the USB port of your PC. Run the following command to compile and upload:
make flash
Follow the instructions on CNLohr's ch32v003fun page to set up the toolchain on your respective operating system (for Windows, use WSL). Also, install Python3 and chprog. Compile and upload with "make flash". Note that I only have Debian-based Linux and have not tested it on other operating systems.
- Install PlatformIO and platform-ch32v. Follow these instructions to do so. Linux/Mac users may also need to install pyenv.
- Click on "Open Project" and select the firmware folder with the platformio.ini file.
- Press the BOOT button and keep it pressed while connecting the board to the USB port of your PC. Then click "Upload".
WCH offers the free but closed-source software WCHISPTool to upload firmware with Windows via the USB bootloader. Press the BOOT button and keep it pressed while connecting the board to the USB port of your PC. Release the BOOT button, open the pd_adapter.hex file in the bin folder with WCHISPTool and upload it to the microcontroller.
If Python3 is installed, you can also use the platform-independent open-source command-line tool chprog for uploading:
chprog bin/pd_adapter.bin
- Connect the USB PD Adapter to a USB Type-C PD power supply using a USB-C cable.
- Use the INC/DEC buttons to select the desired output voltage in steps of 20mV.
- Connect the device to the power consumer via the output screw terminal.
- Use the RST button to clear the energy counter.
- EasyEDA Design Files
- MCU Templates
- MCU Flash Tools
- CH32X035 Datasheets
- INA219 Datasheet
- SSD1306 Datasheet
- HT7533-1 Datasheet
- ATtiny814 USB PD Adapter
- ATtiny412 USB PD Inverter
- CH32X035 USB PD Tester
- TI Primer on USB PD
- CH32X035 F7P6 on Aliexpress
- 128x32 OLED on Aliexpress
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/)