- User can use a Xbox Wireless Controller to steer the rover, tweak the angle of on-board camera.
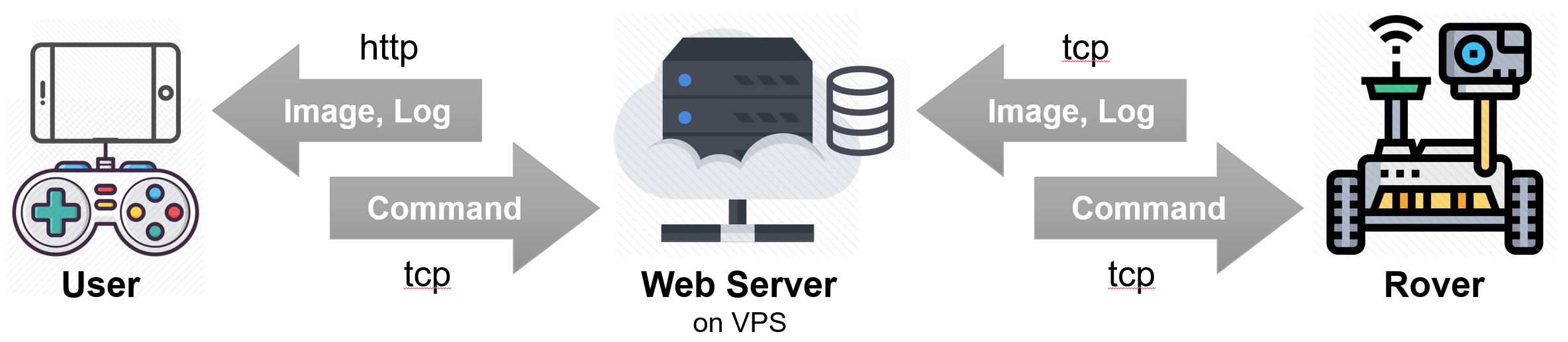
- A website is set up to track the GPS position of rover and display the real-time image captured from the rover.
- The Controller is linked to a Raspberry Pi (RPi) Zero W or PC via Bluetooth.
- Commands came from the Controller are sent to a publicly accessible Web Server.
- The Server forwards processed commands to the Rover, who would move around accordingly.
- Real-time image and sensor reading are sent back to the web server, where the image is stored on the fly while sensor data is processed and logged in a database.
- A web browser of user can access the webpage on server, fetch the latest image and GPS trace, and render them for user's inspection.
- Besides, all communication are protected by SSL
- Raspberry Pi: Zero W
- ESP8266: D1 mini clone (with battery shield)
- Servo: SG90
- GPS: GY-NEO6MV2
- Compass: GY-BNO055
- Camera: Pi Camera
- Motor Driver: PCA9685 + TB6612 DC/Stepper Motor Driver Board
- Register a domain (Google Domain)
- Setup an AWS account and get AWS IAM access credentials.
- Run setup/Use_LightSail_as_Server.ipynb with Access key ID (for example, AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE) and secret access key at hand.
- Log in the server and run setup/secret.sh
ssh -i lightsail -NfR 2222:127.0.0.1:3333 -l ubuntu guoxiaokang.net && raspivid --rotation 90 --timeout 0 --width 640 --height 360 --bitrate 1000000 --framerate 25 --profile baseline --listen -o tcp://127.0.0.1:3333 &- Connect Xbox Wireless Controller to a win10 laptop.
- Enable I2C interface of on-board raspberry pi to communicate with Motor Driver Board
- Install python libraries for on-board raspberry pi
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-pigpio # servo
pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-motorkit # motor- Since additional libraries are needed in Arduino IDE, let's install them on Raspberry Pi
sudo ln -s /home/pi/arduino-1.8.13/arduino /usr/local/bin/arduino
arduino --install-library TinyGPS
arduino --install-library "Adafruit Unified Sensor"
arduino --install-library "Adafruit BNO055"
arduino --board arduino:avr:nano:cpu=atmega328old --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --upload Sensor.ino
- Disconnect VCC pin of GPS breakout before program the arduino board (Uno for testing)
arduino --board arduino:avr:nano:cpu=atmega328old --port /dev/ttyUSB0 --upload Sensor.ino
What I want
- Low latency
- Low burden for the raspberry pi on rover
- Secure video transmission between rover and intermediate server.
- Least library dependency on rover (Install package is a nightmare on raspberry pi)
Solution
- Avoid python and use raspivid
- Redirect stdout (video stream in h264) of raspivid to server via ssh
- Encoding on the intermediate server and then distribute in webm (maybe)
Implement (Proof of concept)
- Capture video and listen on a local port 3333 on raspberry pi (it turned out that there is no noticeable burden on raspberry pi)
raspivid --timeout 0 --width 640 --height 360 --bitrate 1000000 --framerate 25 --profile baseline --listen -o tcp://127.0.0.1:3333- Initiate a remote port forwarding from raspberry pi and listen on port 2222 of remote server
ssh -R 2222:127.0.0.1:3333 remote_server- View the stream from remote_server
ffplay -i tcp://127.0.0.1:2222- Replace Xbox controller with DIYed WIFI controller since it hard to automate Bluetooth pairing.
- Replace Arduino with ESP8266, which is a 3.3v board, to eliminate no logic level converter.
- Communication between Arduino and Raspberry Pi is now in UART to save a USB port
- A mechanical arm is installed.
- A second non-Infrared is added and it can move 360.
- Offload the communication with sensors to Arduino Uno
- TCP Communication can be interrupted by network error and will resume automatically after that.
- All resources are localized if possible.
- Use tcp for the sensor data communication as shown above. The first version actually use http which is expensive for on-board RPi.