Deployment & Documentation & Stats & License
Welcome to PyOD, a well-developed and easy-to-use Python library for detecting anomalies in multivariate data. Whether you are working with a small-scale project or large datasets, PyOD provides a range of algorithms to fit your needs.
PyOD Version 2 is now available (Paper) [11], featuring:
- Expanded Deep Learning Support: Integrates 12 modern neural models into a single PyTorch-based framework, bringing the total number of outlier detection methods to 45.
- Enhanced Performance and Ease of Use: Models are optimized for efficiency and consistent performance across different datasets.
- LLM-based Model Selection: Automated model selection guided by a large language model reduces manual tuning and assists users who may have limited experience with outlier detection.
Additional Resources:
- NLP Anomaly Detection: NLP-ADBench provides both NLP anonaly detection datasets and algorithms
- Time-series Outlier Detection: TODS
- Graph Outlier Detection: PyGOD
- Performance Comparison & Datasets: Our 45-page anomaly detection benchmark paper and ADBench, comparing 30 algorithms on 57 datasets
- PyOD on Distributed Systems: PyOD on Databricks
- Learn More: Anomaly Detection Resources
Check out our latest research in 2025 on LLM-based anomaly detection [48]: AD-LLM: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Anomaly Detection.
PyOD, established in 2017, has become a go-to Python library for detecting anomalous/outlying objects in multivariate data. This exciting yet challenging field is commonly referred to as Outlier Detection or Anomaly Detection.
PyOD includes more than 50 detection algorithms, from classical LOF (SIGMOD 2000) to the cutting-edge ECOD and DIF (TKDE 2022 and 2023). Since 2017, PyOD has been successfully used in numerous academic research projects and commercial products with more than 26 million downloads. It is also well acknowledged by the machine learning community with various dedicated posts/tutorials, including Analytics Vidhya, KDnuggets, and Towards Data Science.
PyOD is featured for:
- Unified, User-Friendly Interface across various algorithms.
- Wide Range of Models, from classic techniques to the latest deep learning methods in PyTorch.
- High Performance & Efficiency, leveraging numba and joblib for JIT compilation and parallel processing.
- Fast Training & Prediction, achieved through the SUOD framework [53].
Outlier Detection with 5 Lines of Code:
# Example: Training an ECOD detector
from pyod.models.ecod import ECOD
clf = ECOD()
clf.fit(X_train)
y_train_scores = clf.decision_scores_ # Outlier scores for training data
y_test_scores = clf.decision_function(X_test) # Outlier scores for test dataSelecting the Right Algorithm: Unsure where to start? Consider these robust and interpretable options:
- ECOD: Example of using ECOD for outlier detection
- Isolation Forest: Example of using Isolation Forest for outlier detection
Alternatively, explore MetaOD for a data-driven approach.
Citing PyOD:
If you use PyOD in a scientific publication, we would appreciate citations to the following paper(s):
PyOD 2: A Python Library for Outlier Detection with LLM-powered Model Selection is available as a preprint. If you use PyOD in a scientific publication, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
@article{zhao2024pyod2,
author = {Chen, Sihan and Qian, Zhuangzhuang and Siu, Wingchun and Hu, Xingcan and Li, Jiaqi and Li, Shawn and Qin, Yuehan and Yang, Tiankai and Xiao, Zhuo and Ye, Wanghao and Zhang, Yichi and Dong, Yushun and Zhao, Yue},
title = {PyOD 2: A Python Library for Outlier Detection with LLM-powered Model Selection},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.12154},
year = {2024}
}
PyOD paper is published in Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR) (MLOSS track).:
@article{zhao2019pyod,
author = {Zhao, Yue and Nasrullah, Zain and Li, Zheng},
title = {PyOD: A Python Toolbox for Scalable Outlier Detection},
journal = {Journal of Machine Learning Research},
year = {2019},
volume = {20},
number = {96},
pages = {1-7},
url = {http://jmlr.org/papers/v20/19-011.html}
}
or:
Zhao, Y., Nasrullah, Z. and Li, Z., 2019. PyOD: A Python Toolbox for Scalable Outlier Detection. Journal of machine learning research (JMLR), 20(96), pp.1-7.
For a broader perspective on anomaly detection, see our NeurIPS papers ADBench: Anomaly Detection Benchmark Paper and ADGym: Design Choices for Deep Anomaly Detection:
@article{han2022adbench,
title={Adbench: Anomaly detection benchmark},
author={Han, Songqiao and Hu, Xiyang and Huang, Hailiang and Jiang, Minqi and Zhao, Yue},
journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume={35},
pages={32142--32159},
year={2022}
}
@article{jiang2023adgym,
title={ADGym: Design Choices for Deep Anomaly Detection},
author={Jiang, Minqi and Hou, Chaochuan and Zheng, Ao and Han, Songqiao and Huang, Hailiang and Wen, Qingsong and Hu, Xiyang and Zhao, Yue},
journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume={36},
year={2023}
}
Table of Contents:
- Installation
- API Cheatsheet & Reference
- ADBench Benchmark and Datasets
- Model Save & Load
- Fast Train with SUOD
- Thresholding Outlier Scores
- Implemented Algorithms
- Quick Start for Outlier Detection
- How to Contribute
- Inclusion Criteria
PyOD is designed for easy installation using either pip or conda. We recommend using the latest version of PyOD due to frequent updates and enhancements:
pip install pyod # normal install
pip install --upgrade pyod # or update if neededconda install -c conda-forge pyodAlternatively, you can clone and run the setup.py file:
git clone https://github.com/yzhao062/pyod.git
cd pyod
pip install .Required Dependencies:
- Python 3.8 or higher
- joblib
- matplotlib
- numpy>=1.19
- numba>=0.51
- scipy>=1.5.1
- scikit_learn>=0.22.0
Optional Dependencies (see details below):
- combo (optional, required for models/combination.py and FeatureBagging)
- pytorch (optional, required for AutoEncoder, and other deep learning models)
- suod (optional, required for running SUOD model)
- xgboost (optional, required for XGBOD)
- pythresh (optional, required for thresholding)
The full API Reference is available at PyOD Documentation. Below is a quick cheatsheet for all detectors:
- fit(X): Fit the detector. The parameter y is ignored in unsupervised methods.
- decision_function(X): Predict raw anomaly scores for X using the fitted detector.
- predict(X): Determine whether a sample is an outlier or not as binary labels using the fitted detector.
- predict_proba(X): Estimate the probability of a sample being an outlier using the fitted detector.
- predict_confidence(X): Assess the model's confidence on a per-sample basis (applicable in predict and predict_proba) [36].
- predict_with_rejection(X): Allow the detector to reject (i.e., abstain from making) highly uncertain predictions (output = -2) [37].
Key Attributes of a fitted model:
- decision_scores_: Outlier scores of the training data. Higher scores typically indicate more abnormal behavior. Outliers usually have higher scores.
- labels_: Binary labels of the training data, where 0 indicates inliers and 1 indicates outliers/anomalies.
We just released a 45-page, the most comprehensive ADBench: Anomaly Detection Benchmark [16]. The fully open-sourced ADBench compares 30 anomaly detection algorithms on 57 benchmark datasets.
The organization of ADBench is provided below:

For a simpler visualization, we make the comparison of selected models via compare_all_models.py.

PyOD takes a similar approach of sklearn regarding model persistence. See model persistence for clarification.
In short, we recommend to use joblib or pickle for saving and loading PyOD models. See "examples/save_load_model_example.py" for an example. In short, it is simple as below:
from joblib import dump, load
# save the model
dump(clf, 'clf.joblib')
# load the model
clf = load('clf.joblib')It is known that there are challenges in saving neural network models. Check #328 and #88 for temporary workaround.
Fast training and prediction: it is possible to train and predict with a large number of detection models in PyOD by leveraging SUOD framework [53]. See SUOD Paper and SUOD example.
from pyod.models.suod import SUOD
# initialized a group of outlier detectors for acceleration
detector_list = [LOF(n_neighbors=15), LOF(n_neighbors=20),
LOF(n_neighbors=25), LOF(n_neighbors=35),
COPOD(), IForest(n_estimators=100),
IForest(n_estimators=200)]
# decide the number of parallel process, and the combination method
# then clf can be used as any outlier detection model
clf = SUOD(base_estimators=detector_list, n_jobs=2, combination='average',
verbose=False)A more data-based approach can be taken when setting the contamination level. By using a thresholding method, guessing an arbitrary value can be replaced with tested techniques for separating inliers and outliers. Refer to PyThresh for a more in-depth look at thresholding.
from pyod.models.knn import KNN
from pyod.models.thresholds import FILTER
# Set the outlier detection and thresholding methods
clf = KNN(contamination=FILTER())See supported thresholding methods in thresholding.
PyOD toolkit consists of four major functional groups:
(i) Individual Detection Algorithms :
| Type | Abbr | Algorithm | Year | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probabilistic | ECOD | Unsupervised Outlier Detection Using Empirical Cumulative Distribution Functions | 2022 | [29] |
| Probabilistic | ABOD | Angle-Based Outlier Detection | 2008 | [23] |
| Probabilistic | FastABOD | Fast Angle-Based Outlier Detection using approximation | 2008 | [23] |
| Probabilistic | COPOD | COPOD: Copula-Based Outlier Detection | 2020 | [28] |
| Probabilistic | MAD | Median Absolute Deviation (MAD) | 1993 | [20] |
| Probabilistic | SOS | Stochastic Outlier Selection | 2012 | [21] |
| Probabilistic | QMCD | Quasi-Monte Carlo Discrepancy outlier detection | 2001 | [12] |
| Probabilistic | KDE | Outlier Detection with Kernel Density Functions | 2007 | [25] |
| Probabilistic | Sampling | Rapid distance-based outlier detection via sampling | 2013 | [44] |
| Probabilistic | GMM | Probabilistic Mixture Modeling for Outlier Analysis | [1] [Ch.2] | |
| Linear Model | PCA | Principal Component Analysis (the sum of weighted projected distances to the eigenvector hyperplanes) | 2003 | [43] |
| Linear Model | KPCA | Kernel Principal Component Analysis | 2007 | [19] |
| Linear Model | MCD | Minimum Covariance Determinant (use the mahalanobis distances as the outlier scores) | 1999 | [17] [39] |
| Linear Model | CD | Use Cook's distance for outlier detection | 1977 | [10] |
| Linear Model | OCSVM | One-Class Support Vector Machines | 2001 | [42] |
| Linear Model | LMDD | Deviation-based Outlier Detection (LMDD) | 1996 | [6] |
| Proximity-Based | LOF | Local Outlier Factor | 2000 | [8] |
| Proximity-Based | COF | Connectivity-Based Outlier Factor | 2002 | [45] |
| Proximity-Based | (Incremental) COF | Memory Efficient Connectivity-Based Outlier Factor (slower but reduce storage complexity) | 2002 | [45] |
| Proximity-Based | CBLOF | Clustering-Based Local Outlier Factor | 2003 | [18] |
| Proximity-Based | LOCI | LOCI: Fast outlier detection using the local correlation integral | 2003 | [34] |
| Proximity-Based | HBOS | Histogram-based Outlier Score | 2012 | [13] |
| Proximity-Based | kNN | k Nearest Neighbors (use the distance to the kth nearest neighbor as the outlier score) | 2000 | [38] |
| Proximity-Based | AvgKNN | Average kNN (use the average distance to k nearest neighbors as the outlier score) | 2002 | [5] |
| Proximity-Based | MedKNN | Median kNN (use the median distance to k nearest neighbors as the outlier score) | 2002 | [5] |
| Proximity-Based | SOD | Subspace Outlier Detection | 2009 | [24] |
| Proximity-Based | ROD | Rotation-based Outlier Detection | 2020 | [4] |
| Outlier Ensembles | IForest | Isolation Forest | 2008 | [30] |
| Outlier Ensembles | INNE | Isolation-based Anomaly Detection Using Nearest-Neighbor Ensembles | 2018 | [7] |
| Outlier Ensembles | DIF | Deep Isolation Forest for Anomaly Detection | 2023 | [47] |
| Outlier Ensembles | FB | Feature Bagging | 2005 | [26] |
| Outlier Ensembles | LSCP | LSCP: Locally Selective Combination of Parallel Outlier Ensembles | 2019 | [52] |
| Outlier Ensembles | XGBOD | Extreme Boosting Based Outlier Detection (Supervised) | 2018 | [51] |
| Outlier Ensembles | LODA | Lightweight On-line Detector of Anomalies | 2016 | [35] |
| Outlier Ensembles | SUOD | SUOD: Accelerating Large-scale Unsupervised Heterogeneous Outlier Detection (Acceleration) | 2021 | [53] |
| Neural Networks | AutoEncoder | Fully connected AutoEncoder (use reconstruction error as the outlier score) | [1] [Ch.3] | |
| Neural Networks | VAE | Variational AutoEncoder (use reconstruction error as the outlier score) | 2013 | [22] |
| Neural Networks | Beta-VAE | Variational AutoEncoder (all customized loss term by varying gamma and capacity) | 2018 | [9] |
| Neural Networks | SO_GAAL | Single-Objective Generative Adversarial Active Learning | 2019 | [31] |
| Neural Networks | MO_GAAL | Multiple-Objective Generative Adversarial Active Learning | 2019 | [31] |
| Neural Networks | DeepSVDD | Deep One-Class Classification | 2018 | [40] |
| Neural Networks | AnoGAN | Anomaly Detection with Generative Adversarial Networks | 2017 | [41] |
| Neural Networks | ALAD | Adversarially learned anomaly detection | 2018 | [50] |
| Neural Networks | AE1SVM | Autoencoder-based One-class Support Vector Machine | 2019 | [32] |
| Neural Networks | DevNet | Deep Anomaly Detection with Deviation Networks | 2019 | [33] |
| Graph-based | R-Graph | Outlier detection by R-graph | 2017 | [49] |
| Graph-based | LUNAR | LUNAR: Unifying Local Outlier Detection Methods via Graph Neural Networks | 2022 | [14] |
(ii) Outlier Ensembles & Outlier Detector Combination Frameworks:
| Type | Abbr | Algorithm | Year | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outlier Ensembles | FB | Feature Bagging | 2005 | [26] |
| Outlier Ensembles | LSCP | LSCP: Locally Selective Combination of Parallel Outlier Ensembles | 2019 | [52] |
| Outlier Ensembles | XGBOD | Extreme Boosting Based Outlier Detection (Supervised) | 2018 | [51] |
| Outlier Ensembles | LODA | Lightweight On-line Detector of Anomalies | 2016 | [35] |
| Outlier Ensembles | SUOD | SUOD: Accelerating Large-scale Unsupervised Heterogeneous Outlier Detection (Acceleration) | 2021 | [53] |
| Outlier Ensembles | INNE | Isolation-based Anomaly Detection Using Nearest-Neighbor Ensembles | 2018 | [7] |
| Combination | Average | Simple combination by averaging the scores | 2015 | [2] |
| Combination | Weighted Average | Simple combination by averaging the scores with detector weights | 2015 | [2] |
| Combination | Maximization | Simple combination by taking the maximum scores | 2015 | [2] |
| Combination | AOM | Average of Maximum | 2015 | [2] |
| Combination | MOA | Maximization of Average | 2015 | [2] |
| Combination | Median | Simple combination by taking the median of the scores | 2015 | [2] |
| Combination | majority Vote | Simple combination by taking the majority vote of the labels (weights can be used) | 2015 | [2] |
(iii) Utility Functions:
| Type | Name | Function | Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data | generate_data | Synthesized data generation; normal data is generated by a multivariate Gaussian and outliers are generated by a uniform distribution | generate_data |
| Data | generate_data_clusters | Synthesized data generation in clusters; more complex data patterns can be created with multiple clusters | generate_data_clusters |
| Stat | wpearsonr | Calculate the weighted Pearson correlation of two samples | wpearsonr |
| Utility | get_label_n | Turn raw outlier scores into binary labels by assign 1 to top n outlier scores | get_label_n |
| Utility | precision_n_scores | calculate precision @ rank n | precision_n_scores |
PyOD has been well acknowledged by the machine learning community with a few featured posts and tutorials.
Analytics Vidhya: An Awesome Tutorial to Learn Outlier Detection in Python using PyOD Library
KDnuggets: Intuitive Visualization of Outlier Detection Methods, An Overview of Outlier Detection Methods from PyOD
Towards Data Science: Anomaly Detection for Dummies
"examples/knn_example.py" demonstrates the basic API of using kNN detector. It is noted that the API across all other algorithms are consistent/similar.
More detailed instructions for running examples can be found in examples directory.
Initialize a kNN detector, fit the model, and make the prediction.
from pyod.models.knn import KNN # kNN detector # train kNN detector clf_name = 'KNN' clf = KNN() clf.fit(X_train) # get the prediction label and outlier scores of the training data y_train_pred = clf.labels_ # binary labels (0: inliers, 1: outliers) y_train_scores = clf.decision_scores_ # raw outlier scores # get the prediction on the test data y_test_pred = clf.predict(X_test) # outlier labels (0 or 1) y_test_scores = clf.decision_function(X_test) # outlier scores # it is possible to get the prediction confidence as well y_test_pred, y_test_pred_confidence = clf.predict(X_test, return_confidence=True) # outlier labels (0 or 1) and confidence in the range of [0,1]
Evaluate the prediction by ROC and Precision @ Rank n (p@n).
from pyod.utils.data import evaluate_print # evaluate and print the results print("\nOn Training Data:") evaluate_print(clf_name, y_train, y_train_scores) print("\nOn Test Data:") evaluate_print(clf_name, y_test, y_test_scores)
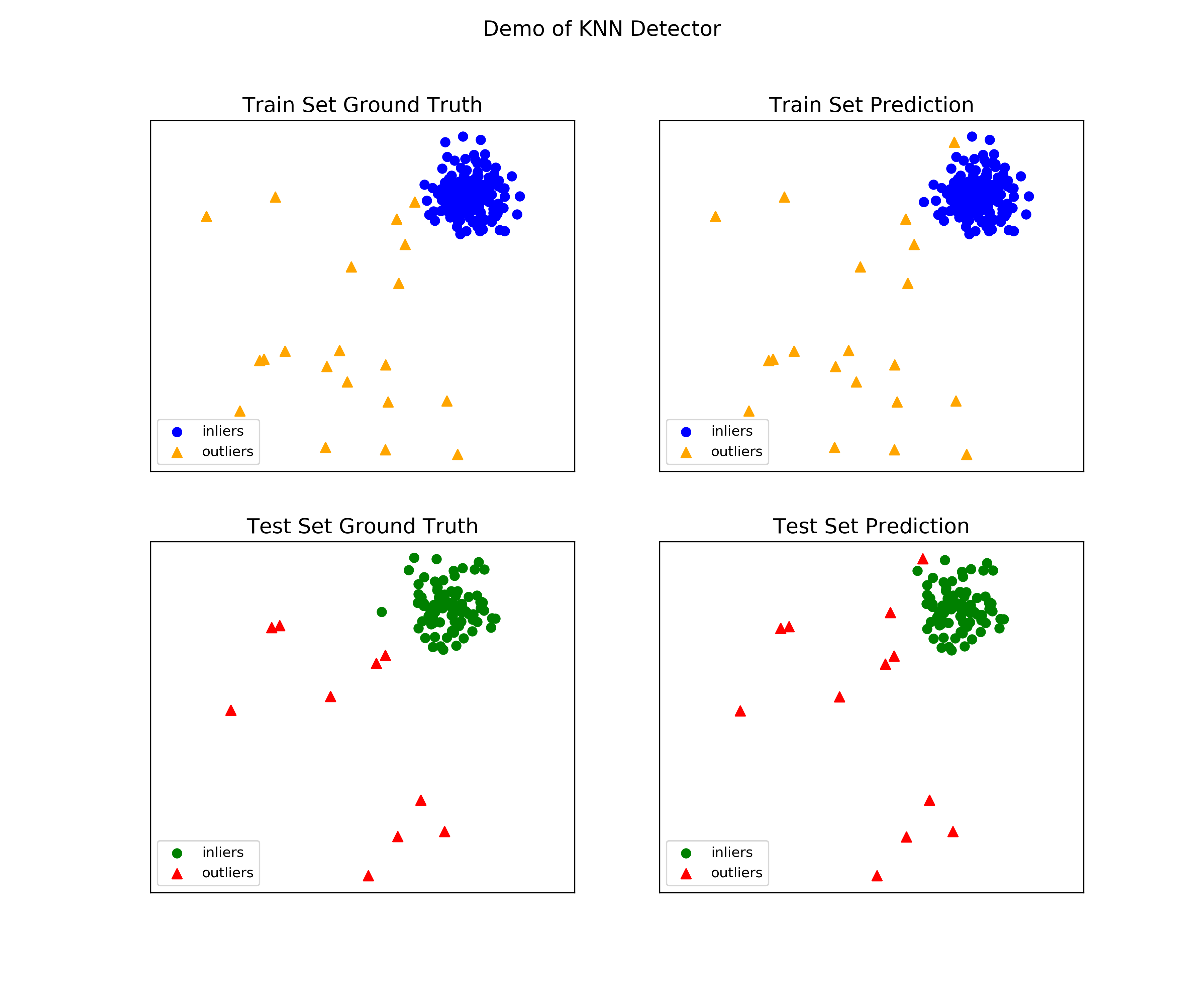
See a sample output & visualization.
On Training Data: KNN ROC:1.0, precision @ rank n:1.0 On Test Data: KNN ROC:0.9989, precision @ rank n:0.9
visualize(clf_name, X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, y_train_pred, y_test_pred, show_figure=True, save_figure=False)
Visualization (knn_figure):
| [1] | (1, 2) Aggarwal, C.C., 2015. Outlier analysis. In Data mining (pp. 237-263). Springer, Cham. |
| [2] | (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) Aggarwal, C.C. and Sathe, S., 2015. Theoretical foundations and algorithms for outlier ensembles.ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 17(1), pp.24-47. |
| [3] | Aggarwal, C.C. and Sathe, S., 2017. Outlier ensembles: An introduction. Springer. |
| [4] | Almardeny, Y., Boujnah, N. and Cleary, F., 2020. A Novel Outlier Detection Method for Multivariate Data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering. |
| [5] | (1, 2) Angiulli, F. and Pizzuti, C., 2002, August. Fast outlier detection in high dimensional spaces. In European Conference on Principles of Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery pp. 15-27. |
| [6] | Arning, A., Agrawal, R. and Raghavan, P., 1996, August. A Linear Method for Deviation Detection in Large Databases. In KDD (Vol. 1141, No. 50, pp. 972-981). |
| [7] | (1, 2) Bandaragoda, T. R., Ting, K. M., Albrecht, D., Liu, F. T., Zhu, Y., and Wells, J. R., 2018, Isolation-based anomaly detection using nearest-neighbor ensembles. Computational Intelligence, 34(4), pp. 968-998. |
| [8] | Breunig, M.M., Kriegel, H.P., Ng, R.T. and Sander, J., 2000, May. LOF: identifying density-based local outliers. ACM Sigmod Record, 29(2), pp. 93-104. |
| [9] | Burgess, Christopher P., et al. "Understanding disentangling in beta-VAE." arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03599 (2018). |
| [10] | Cook, R.D., 1977. Detection of influential observation in linear regression. Technometrics, 19(1), pp.15-18. |
| [11] | Chen, S., Qian, Z., Siu, W., Hu, X., Li, J., Li, S., Qin, Y., Yang, T., Xiao, Z., Ye, W. and Zhang, Y., 2024. PyOD 2: A Python Library for Outlier Detection with LLM-powered Model Selection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.12154. |
| [12] | Fang, K.T. and Ma, C.X., 2001. Wrap-around L2-discrepancy of random sampling, Latin hypercube and uniform designs. Journal of complexity, 17(4), pp.608-624. |
| [13] | Goldstein, M. and Dengel, A., 2012. Histogram-based outlier score (hbos): A fast unsupervised anomaly detection algorithm. In KI-2012: Poster and Demo Track, pp.59-63. |
| [14] | Goodge, A., Hooi, B., Ng, S.K. and Ng, W.S., 2022, June. Lunar: Unifying local outlier detection methods via graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. |
| [15] | Gopalan, P., Sharan, V. and Wieder, U., 2019. PIDForest: Anomaly Detection via Partial Identification. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 15783-15793. |
| [16] | Han, S., Hu, X., Huang, H., Jiang, M. and Zhao, Y., 2022. ADBench: Anomaly Detection Benchmark. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.09426. |
| [17] | Hardin, J. and Rocke, D.M., 2004. Outlier detection in the multiple cluster setting using the minimum covariance determinant estimator. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 44(4), pp.625-638. |
| [18] | He, Z., Xu, X. and Deng, S., 2003. Discovering cluster-based local outliers. Pattern Recognition Letters, 24(9-10), pp.1641-1650. |
| [19] | Hoffmann, H., 2007. Kernel PCA for novelty detection. Pattern recognition, 40(3), pp.863-874. |
| [20] | Iglewicz, B. and Hoaglin, D.C., 1993. How to detect and handle outliers (Vol. 16). Asq Press. |
| [21] | Janssens, J.H.M., Huszár, F., Postma, E.O. and van den Herik, H.J., 2012. Stochastic outlier selection. Technical report TiCC TR 2012-001, Tilburg University, Tilburg Center for Cognition and Communication, Tilburg, The Netherlands. |
| [22] | Kingma, D.P. and Welling, M., 2013. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6114. |
| [23] | (1, 2) Kriegel, H.P. and Zimek, A., 2008, August. Angle-based outlier detection in high-dimensional data. In KDD '08, pp. 444-452. ACM. |
| [24] | Kriegel, H.P., Kröger, P., Schubert, E. and Zimek, A., 2009, April. Outlier detection in axis-parallel subspaces of high dimensional data. In Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 831-838. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| [25] | Latecki, L.J., Lazarevic, A. and Pokrajac, D., 2007, July. Outlier detection with kernel density functions. In International Workshop on Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition (pp. 61-75). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| [26] | (1, 2) Lazarevic, A. and Kumar, V., 2005, August. Feature bagging for outlier detection. In KDD '05. 2005. |
| [27] | Li, D., Chen, D., Jin, B., Shi, L., Goh, J. and Ng, S.K., 2019, September. MAD-GAN: Multivariate anomaly detection for time series data with generative adversarial networks. In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (pp. 703-716). Springer, Cham. |
| [28] | Li, Z., Zhao, Y., Botta, N., Ionescu, C. and Hu, X. COPOD: Copula-Based Outlier Detection. IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), 2020. |
| [29] | Li, Z., Zhao, Y., Hu, X., Botta, N., Ionescu, C. and Chen, H. G. ECOD: Unsupervised Outlier Detection Using Empirical Cumulative Distribution Functions. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering (TKDE), 2022. |
| [30] | Liu, F.T., Ting, K.M. and Zhou, Z.H., 2008, December. Isolation forest. In International Conference on Data Mining, pp. 413-422. IEEE. |
| [31] | (1, 2) Liu, Y., Li, Z., Zhou, C., Jiang, Y., Sun, J., Wang, M. and He, X., 2019. Generative adversarial active learning for unsupervised outlier detection. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering. |
| [32] | Nguyen, M.N. and Vien, N.A., 2019. Scalable and interpretable one-class svms with deep learning and random fourier features. In Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases: European Conference, ECML PKDD, 2018. |
| [33] | Pang, Guansong, Chunhua Shen, and Anton Van Den Hengel. "Deep anomaly detection with deviation networks." In KDD, pp. 353-362. 2019. |
| [34] | Papadimitriou, S., Kitagawa, H., Gibbons, P.B. and Faloutsos, C., 2003, March. LOCI: Fast outlier detection using the local correlation integral. In ICDE '03, pp. 315-326. IEEE. |
| [35] | (1, 2) Pevný, T., 2016. Loda: Lightweight on-line detector of anomalies. Machine Learning, 102(2), pp.275-304. |
| [36] | Perini, L., Vercruyssen, V., Davis, J. Quantifying the confidence of anomaly detectors in their example-wise predictions. In Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML-PKDD), 2020. |
| [37] | Perini, L., Davis, J. Unsupervised anomaly detection with rejection. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Seven Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2023. |
| [38] | Ramaswamy, S., Rastogi, R. and Shim, K., 2000, May. Efficient algorithms for mining outliers from large data sets. ACM Sigmod Record, 29(2), pp. 427-438. |
| [39] | Rousseeuw, P.J. and Driessen, K.V., 1999. A fast algorithm for the minimum covariance determinant estimator. Technometrics, 41(3), pp.212-223. |
| [40] | Ruff, L., Vandermeulen, R., Goernitz, N., Deecke, L., Siddiqui, S.A., Binder, A., Müller, E. and Kloft, M., 2018, July. Deep one-class classification. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 4393-4402). PMLR. |
| [41] | Schlegl, T., Seeböck, P., Waldstein, S.M., Schmidt-Erfurth, U. and Langs, G., 2017, June. Unsupervised anomaly detection with generative adversarial networks to guide marker discovery. In International conference on information processing in medical imaging (pp. 146-157). Springer, Cham. |
| [42] | Scholkopf, B., Platt, J.C., Shawe-Taylor, J., Smola, A.J. and Williamson, R.C., 2001. Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution. Neural Computation, 13(7), pp.1443-1471. |
| [43] | Shyu, M.L., Chen, S.C., Sarinnapakorn, K. and Chang, L., 2003. A novel anomaly detection scheme based on principal component classifier. MIAMI UNIV CORAL GABLES FL DEPT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING. |
| [44] | Sugiyama, M. and Borgwardt, K., 2013. Rapid distance-based outlier detection via sampling. Advances in neural information processing systems, 26. |
| [45] | (1, 2) Tang, J., Chen, Z., Fu, A.W.C. and Cheung, D.W., 2002, May. Enhancing effectiveness of outlier detections for low density patterns. In Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 535-548. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. |
| [46] | Wang, X., Du, Y., Lin, S., Cui, P., Shen, Y. and Yang, Y., 2019. adVAE: A self-adversarial variational autoencoder with Gaussian anomaly prior knowledge for anomaly detection. Knowledge-Based Systems. |
| [47] | Xu, H., Pang, G., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., 2023. Deep isolation forest for anomaly detection. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering. |
| [48] | Yang, T., Nian, Y., Li, S., Xu, R., Li, Y., Li, J., Xiao, Z., Hu, X., Rossi, R., Ding, K. and Hu, X., 2024. AD-LLM: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Anomaly Detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.11142. |
| [49] | You, C., Robinson, D.P. and Vidal, R., 2017. Provable self-representation based outlier detection in a union of subspaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. |
| [50] | Zenati, H., Romain, M., Foo, C.S., Lecouat, B. and Chandrasekhar, V., 2018, November. Adversarially learned anomaly detection. In 2018 IEEE International conference on data mining (ICDM) (pp. 727-736). IEEE. |
| [51] | (1, 2) Zhao, Y. and Hryniewicki, M.K. XGBOD: Improving Supervised Outlier Detection with Unsupervised Representation Learning. IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2018. |
| [52] | (1, 2) Zhao, Y., Nasrullah, Z., Hryniewicki, M.K. and Li, Z., 2019, May. LSCP: Locally selective combination in parallel outlier ensembles. In Proceedings of the 2019 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM), pp. 585-593. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. |
| [53] | (1, 2, 3, 4) Zhao, Y., Hu, X., Cheng, C., Wang, C., Wan, C., Wang, W., Yang, J., Bai, H., Li, Z., Xiao, C., Wang, Y., Qiao, Z., Sun, J. and Akoglu, L. (2021). SUOD: Accelerating Large-scale Unsupervised Heterogeneous Outlier Detection. Conference on Machine Learning and Systems (MLSys). |




