-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 54
Gearboxes
TwistedTail edited this page Feb 12, 2021
·
1 revision
- As simple as it gets for gearboxes, these have a higher torque limit compared to other gearbox shapes of the same size.
- Put the power into the big bell end, and it comes out the small end.
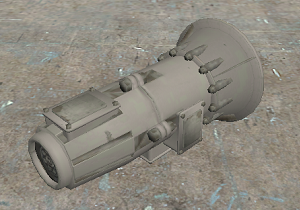
- A quick way to split power between 2 outputs, its very handy for tight applications.
- Put the power into the part that is sticking out, and it comes out both ends on the longer part.

- Another quick way to split power between 2 outputs, except to the left and right of the input.
- Looking at it like a T, the input is the single side, and the outputs are on the sides.

- Sorta the same as the Straight, except it has a single gear, very high torque limit, and is just the bell portion.

- The standard go-to gearbox, these have the aforementioned gear counts.
- Having more gears lets you more gently get to higher speeds, but more gears comes at the cost of a lower torque limit.
- This has 2 gears, commonly referred to as High and Low.
- In tanks, this can be used as a way to do neutral steering by having one gear forward (1), and the other backwards (-1).
- In cars, this is useful to easily get more torque from an engine by having a lower ratio (hence Low)
- This is a special attachment to certain gearboxes which enables you to independently clutch and brake each side, making it easier to steer.
- A special differential capable of independently applying power to each side, as well as enabling neutral steering on its own.
- It has a special input, Steer Rate, which enables the gearbox to control the speed of either side of the gearbox independently.
- If the Steer Rate is within 0 to 0.5 (and negative) it will slow down that side of the gearbox until it reaches 0.5 (-0.5) at which it will stop that side.
- From 0.5 to 1 (and negative) it will then apply power again, IN REVERSE, up to 1 (-1) which is full speed reverse on that side.
- This also has the Double Clutch parts so you can independently clutch and brake each side.
- A gearbox that is capable of shifting on its own, while just requiring you to set the speeds that it shifts at.
- The menu has a nice calculator which can automatically set these speeds.
- This also comes with some extra wire inputs like shift scale that adjusts the speeds when the gearbox will shift, as well as a hold gear input, which just holds the gear it is at.
- Due to the complexity of the gearbox, it loses about 10% torque.
- A box full of belts, this gearbox is capable of keeping an engine within a specified RPM range by constantly adjusting the ratio of the gearbox.
- You specify a minimum and maximum RPM, and the gearbox will adjust its first ratio to keep the input RPM within the ranges.
- This kind of gearbox is rather heavy, and has a lower torque limit.

References
- Ammo Types
- Ammo Crates
- Armor Basics
- Console Variables
- Engines
- Gearboxes
- Guidance Devices
- Guidance Modes
- Hooks (WIP!)
- Radars
- Weaponry
- Turrets
Guides and Tutorials
Resources