-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 100
How to Optimize a Continuous Function
Yu-Ren Liu edited this page Jan 8, 2018
·
6 revisions
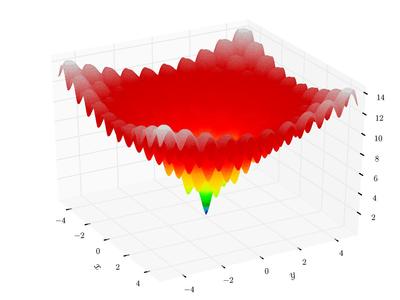
In mathematical optimization, the Ackley function, which has many local minima, is a non-convex function used as a performance test problem for optimization algorithms. In 2-dimension, it looks like (from wikipedia)
 |
We define the Ackley function in simple_function.py for minimization
import numpy as np
def ackley(solution):
"""
Ackley function for continuous optimization
"""
x = solution.get_x()
bias = 0.2
ave_seq = sum([(i - bias) * (i - bias) for i in x]) / len(x)
ave_cos = sum([np.cos(2.0*np.pi*(i-bias)) for i in x]) / len(x)
value = -20 * np.exp(-0.2 * np.sqrt(ave_seq)) - np.exp(ave_cos) + 20.0 + np.e
return valueThen, define corresponding objective and parameter.
dim_size = 100 # dimensions
dim_regs = [[-1, 1]] * dim_size # dimension range
dim_tys = [True] * dim_size # dimension type : real
dim = Dimension(dim_size, dim_regs, dim_tys) # form up the dimension object
objective = Objective(ackley, dim) # form up the objective functionbudget = 100 * dim_size # number of calls to the objective function
parameter = Parameter(budget=budget)Finally, optimize this function.
solution_list = ExpOpt.min(objective, parameter, repeat=1, plot=True)The whole process lists below.
from simple_function import ackley
from zoopt import Dimension, Objective, Parameter, ExpOpt
def minimize_ackley_continuous():
"""
Continuous optimization example of minimizing the ackley function.
:return: no return value
"""
dim_size = 100 # dimensions
dim_regs = [[-1, 1]] * dim_size # dimension range
dim_tys = [True] * dim_size # dimension type : real
dim = Dimension(dim_size, dim_regs, dim_tys) # form up the dimension object
objective = Objective(ackley, dim) # form up the objective function
budget = 100 * dim_size # number of calls to the objective function
parameter = Parameter(budget=budget)
solution_list = ExpOpt.min(objective, parameter, repeat=1, plot=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
minimize_ackley_continuous()For a few seconds, the optimization is done. Visualized optimization progress looks like
 |
More concrete examples are available in the example/simple_functions/continuous_opt.py file .