-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 100
Quick Start
ZOOpt is a python package of Zeroth-Order Optimization.
This package requires the following packages:
- Python version 2.7 or 3.5
-
numpyhttp://www.numpy.org -
matplotlibhttp://matplotlib.org/ (optional for plot drawing)
The easiest way to get these is to use pip or conda environment manager. Typing the following command in your terminal will install all required packages in your Python environment.
$ conda install numpy matplotlib
or
$ pip install numpy matplotlib
The easiest way to get ZOOpt is to type pip install zoopt in you terminal/command line.
If you want to install ZOOpt by source code, download this project and sequentially run following commands in your terminal/command line.
$ python setup.py build
$ python setup.py install
We define the Ackley function for minimization (note that this function is for arbitrary dimensions, determined by the solution)
def ackley(solution):
"""Ackley function for continuous optimization"""
x = solution.get_x()
bias = 0.2
ave_seq = sum([(i - bias) * (i - bias) for i in x]) / len(x)
ave_cos = sum([np.cos(2.0*np.pi*(i-bias)) for i in x]) / len(x)
value = -20 * np.exp(-0.2 * np.sqrt(ave_seq)) - np.exp(ave_cos) + 20.0 + np.e
return valueAckley function is a classical function with many local minima. In 2-dimension, it looks like (from wikipedia)
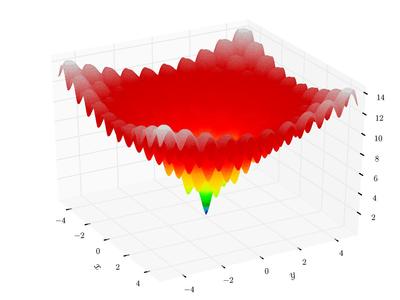 |
We then use ZOOpt to optimize a 100-dimension Ackley function:
- import components from zoopt, where
ExpOptis the experiment-purpose replacement ofOpt
from zoopt import Dimension, Objective, Parameter, ExpOpt- set the dimension
dim = 100 # dimension- setup the
Dimensionobject
dimobj = Dimension(dim, [[-1, 1]] * dim, [True] * dim)- setup the
Objectiveobject defining the function to be minimized
objective = Objective(ackley, dimobj) - setup the parameters of the optimization algorithms. The minimum variable is the budget size
parameter = Parameter(budget=100 * dim)- perform the optimization by
solution = Opt.min(objective, parameter)or using the ExpOpt (from v0.2) for experiments, supporting multi-repeat and ploting,
solution_list = ExpOpt.min(objective, parameter, repeat=1, plot=True) Finally the whole piece of the code for optimization is:
from zoopt import Dimension, Objective, Parameter, ExpOpt
if __name__ == '__main__':
dim = 100 # dimension
objective = Objective(ackley, Dimension(dim, [[-1, 1]] * dim, [True] * dim)) # setup objective
parameter = Parameter(budget=100 * dim)
solution_list = ExpOpt.min(objective, parameter, repeat=1, plot=True) For a few seconds, the optimization is done. The terminal/command line will show optimization result
 |
 |
The rest of the tutorial introduces more functions of ZOOpt.